Shenzhen Xingtong IOT Technology Co., Ltd.
Barcode Scanner Manufacturer with development & Invention ability

Do you really understand QR codes?
Today we're going to talk about one thing that is very closely related to our daily life today - we travel, eat, shop, and probably use it almost every day. That's right, it's a QR code.
Once upon a time, who could have predicted that a small black and white code could have such a wide range of uses, and who could have predicted that this seemingly ordinary black and white square is subtly changing our lives?
Scan the code to add friends: Expand your social circle anytime, anywhere.
Scan code payment: Now even the uncles who sell fruits on the roadside are collecting money on WeChat and Alipay. If you still stubbornly pay with cash, it is really "out".
Itinerary tracking code: Since the epidemic, the personal one-pass code, as the key electronic certificate for personal travel during the epidemic control period, has laid a solid foundation for epidemic prevention and circulation, and is an important guarantee for the safety of citizens.
These are just the most common application scenarios of QR codes. Common ones include scanning to obtain electronic product manuals, member management, advertising push, and so on.
Remember when you started using QR codes? Do you understand QR codes? Why do the QR codes we see have three small squares? Let us unravel its mystery today.
The QR code that we widely use now is the QR (Quick Response) code, which first appeared in 1994, and was quickly integrated into our lives after it was introduced into China in 2001.
The composition and principle of QR code
QR codes are transformed from barcodes. It is the most common on commodity packaging. It consists of black and white vertical stripes with different thicknesses. The information of the commodity is hidden in this barcode.
The cashier can get the product information by scanning the barcode, so as to realize the fast checkout. A barcode is a barcode that carries information in one dimension. A 2D code, as the name suggests, carries information in both horizontal and vertical dimensions, so it changes from a bar to a square shape. Whether it is a barcode or a QR code, it is essentially an information portal.
A complete 2D code is composed of several small black squares and small white squares. First, characters such as numbers, letters, and symbols are converted into binary "0" and "1" through certain operation and encoding rules, and then through A series of optimization algorithms get the QR code. The small white squares on the QR code represent binary "0", and the small black squares represent "1".
When the QR code is read, the 01 sequence on the QR code is read through color contrast, and then the binary is converted into characters that we can recognize through numbers, bytes, special characters, mixed codes, Chinese character codes, etc.
The generation of QR codes follows binary coding, and their arrangement is the embodiment of information. Its basic functional areas are divided into:
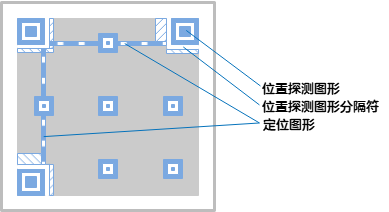
Position detection graphics, position detection graphics separator, and positioning graphics: There is a large black and white square in the three corners of the QR code - the position detection graphics, which together with the position detection graphics separator and positioning graphics help two The dimensional code is positioned during the formation process to reduce the occurrence of wrong arrangement. Whether your phone is scanning horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, it knows which direction the QR code should start to read. For each QR code, their location is fixed, but the size specification will vary.
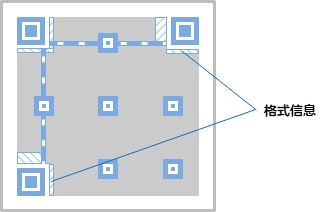
Format information: Indicates the error correction level of the QR code. The higher the level, the stronger the error correction capability. For example, if there are 100 codewords to be encoded, and half of them, that is, 50 codewords, are to be error-corrected, the calculation method is as follows. Error correction requires twice as many symbols as codewords (RS encoding*), so in this case the number is 50 × 2 = 100 codewords. Therefore, the total number of code words is 200, of which 50 are used for error correction, so it is calculated that the error correction rate relative to all code words is 25%. This ratio is equivalent to the "Q" level in the QR code error correction level.
Level L: Up to 7% of characters can be corrected.
Level M: Up to 15% of characters can be corrected.
Level Q: Up to 25% of characters can be corrected.
Level H: Up to 30% of characters can be corrected.
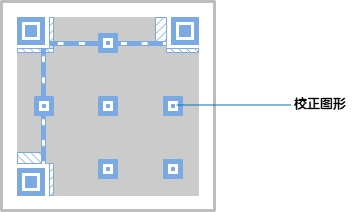
Correction graphics: When the image is damaged to a certain extent, the decoding software can use it to synchronize the coordinate mapping of the image module. The number and position of the QR code correction graphics of different specifications are different. Once the specification is determined, its quantity and location are also determined.
Data and error correction codewords: The actually stored QR code information and error correction codewords. This is a fault-tolerant mechanism for QR codes. For example, if less than 30% of a QR code is covered or removed, the QR code scanner can still accurately obtain information from the incomplete QR code.
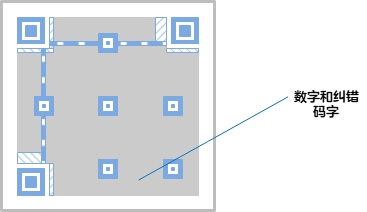
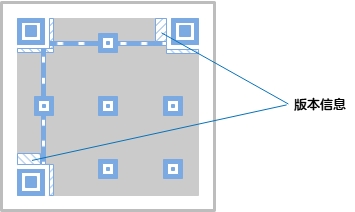
Version information: the specifications of the QR code. The QR code symbol has a matrix of 40 specifications, ranging from 21x21 (version 1) to 177x177 (version 40). Each version has 4 more modules in the vertical and horizontal directions than the previous version. . Each version of the QR code has a corresponding maximum number of input characters in combination with the amount of data, character type and error correction level, which needs to be selected according to actual needs. If the amount of data is increased, more symbols are required, and the QR code will be larger.
When the scan setting starts to scan the QR code, the area to be recognized is quickly extracted according to the position detection pattern, the position detection pattern separator, and the positioning pattern. Sometimes when we scan the QR code with a mobile phone or other device, it is not facing the QR code, or even facing the QR code, it will cause the QR code to be tilted, stretched and other deformations to a certain extent. However, we found that this does not affect the recognition of the QR code, so the correction graphics designed as some fixed-proportion rectangular blocks can help the device to correct the scanned image correctly.
To sum up, the identification process of our QR code is roughly as follows: turn on the mobile phone or other device and scan it to align the QR code. If the scan fails, tell us to go back to the previous step and start over. A scan box is displayed to facilitate users to align the QR code.
Will the QR code be exhausted?
Now that almost every country on the planet uses QR codes every day, and the number of daily use exceeds 10 billion, will QR codes one day be used up? It depends on how many QR codes humans can make.
There are many types of QR codes (QR codes are just one of them, other common ones include QR Code, Code 49, Code 16K, etc.), and each type of QR code can carry a lot of information.
For the same QR code, due to the differences of various versions, each version can carry a lot of information.
QR codes are encoded in different ways and contain different information.
2D codes can be reused. For example, the same 2D code can be used to realize different link jumps, and the same 2D code can be used to allow people to scan different content at different times and places.
The smallest QR code we are currently using is an example, the size is 21×21, which contains 21×21 permutable points, all of which can represent 1 or 0. Therefore, according to the method of permutation and combination, it is 2 to the 441st power. If it is expanded, it is 5.678×10^132. This number is already an astronomical number. Only one version of a QR code with one encoding method can store so much information. At the rate that humans use 10 billion QR codes a day, we don’t have to worry about running out of QR codes.
QR code security issues
While "Living on Code" brings us convenience, security issues also follow. Since QR code generators are easy to obtain from the Internet and have no restrictions on their distribution, they are easily exploited by some criminals to carry out network scams.
Share a real case: When Mr. Li was shopping on Taobao.com, he saw an LCD TV in an online store, and the price was nearly 1,000 yuan cheaper than the one on the market. The owner "Tianma Taoyuan" claimed to be able to get "private goods" at low prices, and Mr. Li accepted the owner's request to make payment by scanning the QR code. After scanning the QR code sent by the store owner with his mobile phone, Mr. Li entered a payment interface, entered the bank account number and password and clicked to pay, but found that the payment failed. The store owner told him that there might be a system failure and told him to rescan. Mr. Li scanned seven times, all of which ended in failure, and had no choice but to cancel the transaction. But then I found that my bank card was deducted more than 17,000 yuan, and it was only at this time that I realized that I had been deceived. Therefore, it is necessary to establish awareness of prevention, improve the understanding of 2D code, and learn to use 2D code correctly.
Liars are cunning, but they don't change their medicine. Be careful when we use it everyday.
The following are some common pitfalls of QR codes, you should be more careful:
QR code scam
Fishing QR code
Get free prizes
and many more
So how can we strengthen the security of QR codes and reduce the risk of scanning codes?
To ensure the security of QR codes, efforts need to be made in the following four aspects:
When enterprises provide QR codes externally, they must ensure the security of QR codes.
When we scan the QR code, firstly, we use the terminal with the function of security identification, and secondly, we must be aware of security and do not scan the QR code from unknown sources.
National legislation protects conduct related to QR code payments.
With the development of technology, there is a "Hanxin code" that is more secure, suitable for Chinese characters, and contains more information.



